#include "cs_defs.h"#include <assert.h>#include <errno.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <stdarg.h>#include <string.h>#include <math.h>#include <float.h>#include "bft_error.h"#include "bft_mem.h"#include "bft_printf.h"#include "cs_bad_cells_regularisation.h"#include "cs_blas.h"#include "cs_cell_to_vertex.h"#include "cs_ext_neighborhood.h"#include "cs_field.h"#include "cs_field_pointer.h"#include "cs_halo.h"#include "cs_halo_perio.h"#include "cs_internal_coupling.h"#include "cs_log.h"#include "cs_math.h"#include "cs_mesh.h"#include "cs_mesh_adjacencies.h"#include "cs_mesh_quantities.h"#include "cs_parall.h"#include "cs_porous_model.h"#include "cs_prototypes.h"#include "cs_timer.h"#include "cs_timer_stats.h"#include "cs_gradient.h"#include "cs_gradient_priv.h" Include dependency graph for cs_gradient.c:
Include dependency graph for cs_gradient.c:Functions | |
| void | grdpor (const int *const inc) |
| void | cgdvec (const int *const f_id, const int *const imrgra, const int *const inc, const int *const n_r_sweeps, const int *const iwarnp, const int *const imligp, const cs_real_t *const epsrgp, const cs_real_t *const climgp, const cs_real_3_t coefav[], const cs_real_33_t coefbv[], cs_real_3_t pvar[], cs_real_33_t grad[]) |
| void | cs_gradient_initialize (void) |
| Initialize gradient computation API. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_finalize (void) |
| Finalize gradient computation API. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_free_quantities (void) |
| Free saved gradient quantities. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_scalar (const char *var_name, cs_gradient_type_t gradient_type, cs_halo_type_t halo_type, int inc, bool recompute_cocg, int n_r_sweeps, int tr_dim, int hyd_p_flag, int w_stride, int verbosity, cs_gradient_limit_t clip_mode, double epsilon, double clip_coeff, cs_real_3_t f_ext[], const cs_real_t bc_coeff_a[], const cs_real_t bc_coeff_b[], cs_real_t var[restrict], cs_real_t *restrict c_weight, const cs_internal_coupling_t *cpl, cs_real_t grad[restrict][3]) |
| Compute cell gradient of scalar field or component of vector or tensor field. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_vector (const char *var_name, cs_gradient_type_t gradient_type, cs_halo_type_t halo_type, int inc, int n_r_sweeps, int verbosity, cs_gradient_limit_t clip_mode, double epsilon, double clip_coeff, const cs_real_t bc_coeff_a[][3], const cs_real_t bc_coeff_b[][3][3], cs_real_t var[restrict][3], cs_real_t *restrict c_weight, const cs_internal_coupling_t *cpl, cs_real_t gradv[restrict][3][3]) |
| Compute cell gradient of vector field. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_tensor (const char *var_name, cs_gradient_type_t gradient_type, cs_halo_type_t halo_type, int inc, int n_r_sweeps, int verbosity, cs_gradient_limit_t clip_mode, double epsilon, double clip_coeff, const cs_real_6_t bc_coeff_a[], const cs_real_66_t bc_coeff_b[], cs_real_6_t *restrict var, cs_real_63_t *restrict grad) |
| Compute cell gradient of tensor. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_scalar_synced_input (const char *var_name, cs_gradient_type_t gradient_type, cs_halo_type_t halo_type, int inc, bool recompute_cocg, int n_r_sweeps, int hyd_p_flag, int w_stride, int verbosity, cs_gradient_limit_t clip_mode, double epsilon, double clip_coeff, cs_real_t f_ext[][3], const cs_real_t bc_coeff_a[], const cs_real_t bc_coeff_b[], const cs_real_t var[restrict], const cs_real_t c_weight[restrict], const cs_internal_coupling_t *cpl, cs_real_t grad[restrict][3]) |
| Compute cell gradient of scalar field or component of vector or tensor field. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_vector_synced_input (const char *var_name, cs_gradient_type_t gradient_type, cs_halo_type_t halo_type, int inc, int n_r_sweeps, int verbosity, cs_gradient_limit_t clip_mode, double epsilon, double clip_coeff, const cs_real_t bc_coeff_a[][3], const cs_real_t bc_coeff_b[][3][3], const cs_real_t var[restrict][3], const cs_real_t c_weight[restrict], const cs_internal_coupling_t *cpl, cs_real_t grad[restrict][3][3]) |
| Compute cell gradient of vector field. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_tensor_synced_input (const char *var_name, cs_gradient_type_t gradient_type, cs_halo_type_t halo_type, int inc, int n_r_sweeps, int verbosity, cs_gradient_limit_t clip_mode, double epsilon, double clip_coeff, const cs_real_t bc_coeff_a[][6], const cs_real_t bc_coeff_b[][6][6], const cs_real_t var[restrict][6], cs_real_63_t *restrict grad) |
| Compute cell gradient of tensor. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_scalar_cell (const cs_mesh_t *m, const cs_mesh_quantities_t *fvq, cs_lnum_t c_id, cs_halo_type_t halo_type, const cs_real_t bc_coeff_a[], const cs_real_t bc_coeff_b[], const cs_real_t var[], const cs_real_t c_weight[], cs_real_t grad[3]) |
| Compute the gradient of a scalar field at a given cell using least-squares reconstruction. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_vector_cell (const cs_mesh_t *m, const cs_mesh_quantities_t *fvq, cs_lnum_t c_id, cs_halo_type_t halo_type, const cs_real_t bc_coeff_a[][3], const cs_real_t bc_coeff_b[][3][3], const cs_real_t var[restrict][3], const cs_real_t c_weight[], cs_real_t grad[3][3]) |
| Compute the gradient of a vector field at a given cell using least-squares reconstruction. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_tensor_cell (const cs_mesh_t *m, const cs_mesh_quantities_t *fvq, cs_lnum_t c_id, cs_halo_type_t halo_type, const cs_real_t bc_coeff_a[][6], const cs_real_t bc_coeff_b[][6][6], const cs_real_t var[restrict][6], const cs_real_t c_weight[], cs_real_t grad[6][3]) |
| Compute the gradient of a tensor field at a given cell using least-squares reconstruction. More... | |
| void | cs_gradient_type_by_imrgra (int imrgra, cs_gradient_type_t *gradient_type, cs_halo_type_t *halo_type) |
| void | cs_gradient_porosity_balance (int inc) |
| compute the steady balance due to porous modelling for the pressure gradient. More... | |
| void cgdvec | ( | const int *const | f_id, |
| const int *const | imrgra, | ||
| const int *const | inc, | ||
| const int *const | n_r_sweeps, | ||
| const int *const | iwarnp, | ||
| const int *const | imligp, | ||
| const cs_real_t *const | epsrgp, | ||
| const cs_real_t *const | climgp, | ||
| const cs_real_3_t | coefav[], | ||
| const cs_real_33_t | coefbv[], | ||
| cs_real_3_t | pvar[], | ||
| cs_real_33_t | grad[] | ||
| ) |
| void cs_gradient_finalize | ( | void | ) |
Finalize gradient computation API.
| void cs_gradient_free_quantities | ( | void | ) |
Free saved gradient quantities.
This is required when the mesh changes, so that the on-demand computation will be updated.
| void cs_gradient_initialize | ( | void | ) |
Initialize gradient computation API.
| void cs_gradient_porosity_balance | ( | int | inc | ) |
compute the steady balance due to porous modelling for the pressure gradient.
| [in] | inc | if 0, solve on increment; 1 otherwise |
| void cs_gradient_scalar | ( | const char * | var_name, |
| cs_gradient_type_t | gradient_type, | ||
| cs_halo_type_t | halo_type, | ||
| int | inc, | ||
| bool | recompute_cocg, | ||
| int | n_r_sweeps, | ||
| int | tr_dim, | ||
| int | hyd_p_flag, | ||
| int | w_stride, | ||
| int | verbosity, | ||
| cs_gradient_limit_t | clip_mode, | ||
| double | epsilon, | ||
| double | clip_coeff, | ||
| cs_real_3_t | f_ext[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_a[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_b[], | ||
| cs_real_t | var[restrict], | ||
| cs_real_t *restrict | c_weight, | ||
| const cs_internal_coupling_t * | cpl, | ||
| cs_real_t | grad[restrict][3] | ||
| ) |
Compute cell gradient of scalar field or component of vector or tensor field.
| [in] | var_name | variable name |
| [in] | gradient_type | gradient type |
| [in] | halo_type | halo type |
| [in] | inc | if 0, solve on increment; 1 otherwise |
| [in] | recompute_cocg | should COCG FV quantities be recomputed ? |
| [in] | n_r_sweeps | if > 1, number of reconstruction sweeps (only used by CS_GRADIENT_GREEN_ITER) |
| [in] | tr_dim | ignored |
| [in] | hyd_p_flag | flag for hydrostatic pressure |
| [in] | w_stride | stride for weighting coefficient |
| [in] | verbosity | verbosity level |
| [in] | clip_mode | clipping mode |
| [in] | epsilon | precision for iterative gradient calculation |
| [in] | clip_coeff | clipping coefficient |
| [in] | f_ext | exterior force generating the hydrostatic pressure |
| [in] | bc_coeff_a | boundary condition term a |
| [in] | bc_coeff_b | boundary condition term b |
| [in,out] | var | gradient's base variable |
| [in,out] | c_weight | cell variable weight, or NULL |
| [in] | cpl | associated internal coupling, or NULL |
| [out] | grad | gradient |
| void cs_gradient_scalar_cell | ( | const cs_mesh_t * | m, |
| const cs_mesh_quantities_t * | fvq, | ||
| cs_lnum_t | c_id, | ||
| cs_halo_type_t | halo_type, | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_a[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_b[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | var[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | c_weight[], | ||
| cs_real_t | grad[3] | ||
| ) |
Compute the gradient of a scalar field at a given cell using least-squares reconstruction.
This assumes ghost cell values which might be used are already synchronized.
When boundary conditions are provided, both the bc_coeff_a and bc_coeff_b arrays must be given. If boundary values are known, bc_coeff_a can point to the boundary values array, and bc_coeff_b set to NULL. If bc_coeff_a is NULL, bc_coeff_b is ignored.
| [in] | m | pointer to associated mesh structure |
| [in] | fvq | pointer to associated finite volume quantities |
| [in] | c_id | cell id |
| [in] | halo_type | halo type |
| [in] | bc_coeff_a | boundary condition term a, or NULL |
| [in] | bc_coeff_b | boundary condition term b, or NULL |
| [in] | var | gradient's base variable |
| [in] | c_weight | cell variable weight, or NULL |
| [out] | grad | gradient |
| void cs_gradient_scalar_synced_input | ( | const char * | var_name, |
| cs_gradient_type_t | gradient_type, | ||
| cs_halo_type_t | halo_type, | ||
| int | inc, | ||
| bool | recompute_cocg, | ||
| int | n_r_sweeps, | ||
| int | hyd_p_flag, | ||
| int | w_stride, | ||
| int | verbosity, | ||
| cs_gradient_limit_t | clip_mode, | ||
| double | epsilon, | ||
| double | clip_coeff, | ||
| cs_real_t | f_ext[][3], | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_a[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_b[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | var[restrict], | ||
| const cs_real_t | c_weight[restrict], | ||
| const cs_internal_coupling_t * | cpl, | ||
| cs_real_t | grad[restrict][3] | ||
| ) |
Compute cell gradient of scalar field or component of vector or tensor field.
This variant of the cs_gradient_scalar function assumes ghost cell values for input arrays (var and optionally c_weight) have already been synchronized.
| [in] | var_name | variable name |
| [in] | gradient_type | gradient type |
| [in] | halo_type | halo type |
| [in] | inc | if 0, solve on increment; 1 otherwise |
| [in] | recompute_cocg | should COCG FV quantities be recomputed ? |
| [in] | n_r_sweeps | if > 1, number of reconstruction sweeps (only used by CS_GRADIENT_GREEN_ITER) |
| [in] | hyd_p_flag | flag for hydrostatic pressure |
| [in] | w_stride | stride for weighting coefficient |
| [in] | verbosity | verbosity level |
| [in] | clip_mode | clipping mode |
| [in] | epsilon | precision for iterative gradient calculation |
| [in] | clip_coeff | clipping coefficient |
| [in] | f_ext | exterior force generating the hydrostatic pressure |
| [in] | bc_coeff_a | boundary condition term a |
| [in] | bc_coeff_b | boundary condition term b |
| [in] | var | gradient's base variable |
| [in] | c_weight | cell variable weight, or NULL |
| [in] | cpl | associated internal coupling, or NULL |
| [out] | grad | gradient |
| void cs_gradient_tensor | ( | const char * | var_name, |
| cs_gradient_type_t | gradient_type, | ||
| cs_halo_type_t | halo_type, | ||
| int | inc, | ||
| int | n_r_sweeps, | ||
| int | verbosity, | ||
| cs_gradient_limit_t | clip_mode, | ||
| double | epsilon, | ||
| double | clip_coeff, | ||
| const cs_real_6_t | bc_coeff_a[], | ||
| const cs_real_66_t | bc_coeff_b[], | ||
| cs_real_6_t *restrict | var, | ||
| cs_real_63_t *restrict | grad | ||
| ) |
Compute cell gradient of tensor.
| [in] | var_name | variable name |
| [in] | gradient_type | gradient type |
| [in] | halo_type | halo type |
| [in] | inc | if 0, solve on increment; 1 otherwise |
| [in] | n_r_sweeps | if > 1, number of reconstruction sweeps (only used by CS_GRADIENT_GREEN_ITER) |
| [in] | verbosity | verbosity level |
| [in] | clip_mode | clipping mode |
| [in] | epsilon | precision for iterative gradient calculation |
| [in] | clip_coeff | clipping coefficient |
| [in] | bc_coeff_a | boundary condition term a |
| [in] | bc_coeff_b | boundary condition term b |
| [in,out] | var | gradient's base variable |
| [out] | grad | gradient ( 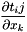 is grad[][ij][k]) is grad[][ij][k]) |
| void cs_gradient_tensor_cell | ( | const cs_mesh_t * | m, |
| const cs_mesh_quantities_t * | fvq, | ||
| cs_lnum_t | c_id, | ||
| cs_halo_type_t | halo_type, | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_a[][6], | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_b[][6][6], | ||
| const cs_real_t | var[restrict][6], | ||
| const cs_real_t | c_weight[], | ||
| cs_real_t | grad[6][3] | ||
| ) |
Compute the gradient of a tensor field at a given cell using least-squares reconstruction.
This assumes ghost cell values which might be used are already synchronized.
When boundary conditions are provided, both the bc_coeff_a and bc_coeff_b arrays must be given. If boundary values are known, bc_coeff_a can point to the boundary values array, and bc_coeff_b set to NULL. If bc_coeff_a is NULL, bc_coeff_b is ignored.
| [in] | m | pointer to associated mesh structure |
| [in] | fvq | pointer to associated finite volume quantities |
| [in] | c_id | cell id |
| [in] | halo_type | halo type |
| [in] | bc_coeff_a | boundary condition term a, or NULL |
| [in] | bc_coeff_b | boundary condition term b, or NULL |
| [in] | var | gradient's base variable |
| [in] | c_weight | cell variable weight, or NULL |
| [out] | grad | gradient |
| void cs_gradient_tensor_synced_input | ( | const char * | var_name, |
| cs_gradient_type_t | gradient_type, | ||
| cs_halo_type_t | halo_type, | ||
| int | inc, | ||
| int | n_r_sweeps, | ||
| int | verbosity, | ||
| cs_gradient_limit_t | clip_mode, | ||
| double | epsilon, | ||
| double | clip_coeff, | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_a[][6], | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_b[][6][6], | ||
| const cs_real_t | var[restrict][6], | ||
| cs_real_63_t *restrict | grad | ||
| ) |
Compute cell gradient of tensor.
This variant of the cs_gradient_tensor function assumes ghost cell values for input arrays (var and optionally c_weight) have already been synchronized.
| [in] | var_name | variable name |
| [in] | gradient_type | gradient type |
| [in] | halo_type | halo type |
| [in] | inc | if 0, solve on increment; 1 otherwise |
| [in] | n_r_sweeps | if > 1, number of reconstruction sweeps (only used by CS_GRADIENT_GREEN_ITER) |
| [in] | verbosity | verbosity level |
| [in] | clip_mode | clipping mode |
| [in] | epsilon | precision for iterative gradient calculation |
| [in] | clip_coeff | clipping coefficient |
| [in] | bc_coeff_a | boundary condition term a |
| [in] | bc_coeff_b | boundary condition term b |
| [in,out] | var | gradient's base variable |
| [out] | grad | gradient ( 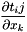 is grad[][ij][k]) is grad[][ij][k]) |
| void cs_gradient_type_by_imrgra | ( | int | imrgra, |
| cs_gradient_type_t * | gradient_type, | ||
| cs_halo_type_t * | halo_type | ||
| ) |
| void cs_gradient_vector | ( | const char * | var_name, |
| cs_gradient_type_t | gradient_type, | ||
| cs_halo_type_t | halo_type, | ||
| int | inc, | ||
| int | n_r_sweeps, | ||
| int | verbosity, | ||
| cs_gradient_limit_t | clip_mode, | ||
| double | epsilon, | ||
| double | clip_coeff, | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_a[][3], | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_b[][3][3], | ||
| cs_real_t | var[restrict][3], | ||
| cs_real_t *restrict | c_weight, | ||
| const cs_internal_coupling_t * | cpl, | ||
| cs_real_t | gradv[restrict][3][3] | ||
| ) |
Compute cell gradient of vector field.
| [in] | var_name | variable name |
| [in] | gradient_type | gradient type |
| [in] | halo_type | halo type |
| [in] | inc | if 0, solve on increment; 1 otherwise |
| [in] | n_r_sweeps | if > 1, number of reconstruction sweeps (only used by CS_GRADIENT_GREEN_ITER) |
| [in] | verbosity | verbosity level |
| [in] | clip_mode | clipping mode |
| [in] | epsilon | precision for iterative gradient calculation |
| [in] | clip_coeff | clipping coefficient |
| [in] | bc_coeff_a | boundary condition term a |
| [in] | bc_coeff_b | boundary condition term b |
| [in,out] | var | gradient's base variable |
| [in,out] | c_weight | cell variable weight, or NULL |
| [in] | cpl | associated internal coupling, or NULL |
| [out] | gradv | gradient ( 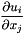 is gradv[][i][j]) is gradv[][i][j]) |
| void cs_gradient_vector_cell | ( | const cs_mesh_t * | m, |
| const cs_mesh_quantities_t * | fvq, | ||
| cs_lnum_t | c_id, | ||
| cs_halo_type_t | halo_type, | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_a[][3], | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_b[][3][3], | ||
| const cs_real_t | var[restrict][3], | ||
| const cs_real_t | c_weight[], | ||
| cs_real_t | grad[3][3] | ||
| ) |
Compute the gradient of a vector field at a given cell using least-squares reconstruction.
This assumes ghost cell values which might be used are already synchronized.
When boundary conditions are provided, both the bc_coeff_a and bc_coeff_b arrays must be given. If boundary values are known, bc_coeff_a can point to the boundary values array, and bc_coeff_b set to NULL. If bc_coeff_a is NULL, bc_coeff_b is ignored.
| [in] | m | pointer to associated mesh structure |
| [in] | fvq | pointer to associated finite volume quantities |
| [in] | c_id | cell id |
| [in] | halo_type | halo type |
| [in] | bc_coeff_a | boundary condition term a, or NULL |
| [in] | bc_coeff_b | boundary condition term b, or NULL |
| [in] | var | gradient's base variable |
| [in] | c_weight | cell variable weight, or NULL |
| [out] | grad | gradient |
| void cs_gradient_vector_synced_input | ( | const char * | var_name, |
| cs_gradient_type_t | gradient_type, | ||
| cs_halo_type_t | halo_type, | ||
| int | inc, | ||
| int | n_r_sweeps, | ||
| int | verbosity, | ||
| cs_gradient_limit_t | clip_mode, | ||
| double | epsilon, | ||
| double | clip_coeff, | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_a[][3], | ||
| const cs_real_t | bc_coeff_b[][3][3], | ||
| const cs_real_t | var[restrict][3], | ||
| const cs_real_t | c_weight[restrict], | ||
| const cs_internal_coupling_t * | cpl, | ||
| cs_real_t | grad[restrict][3][3] | ||
| ) |
Compute cell gradient of vector field.
This variant of the cs_gradient_vector function assumes ghost cell values for input arrays (var and optionally c_weight) have already been synchronized.
| [in] | var_name | variable name |
| [in] | gradient_type | gradient type |
| [in] | halo_type | halo type |
| [in] | inc | if 0, solve on increment; 1 otherwise |
| [in] | n_r_sweeps | if > 1, number of reconstruction sweeps (only used by CS_GRADIENT_GREEN_ITER) |
| [in] | verbosity | verbosity level |
| [in] | clip_mode | clipping mode |
| [in] | epsilon | precision for iterative gradient calculation |
| [in] | clip_coeff | clipping coefficient |
| [in] | bc_coeff_a | boundary condition term a |
| [in] | bc_coeff_b | boundary condition term b |
| [in] | var | gradient's base variable |
| [in] | c_weight | cell variable weight, or NULL |
| [in] | cpl | associated internal coupling, or NULL |
| [out] | grad | gradient ( 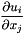 is gradv[][i][j]) is gradv[][i][j]) |
| void grdpor | ( | const int *const | inc | ) |