#include "cs_base.h"#include "cs_domain.h"#include "cs_field.h"#include "cs_mesh.h"#include "cs_mesh_quantities.h"#include "cs_mesh_bad_cells.h"#include "cs_probe.h"#include "cs_volume_zone.h" Include dependency graph for cs_prototypes.h:
Include dependency graph for cs_prototypes.h:Go to the source code of this file.
Functions | |
| void | caltri (void) |
| void | cs_hydrostatic_pressure_compute (int *indhyd, int iterns, cs_real_t fext[][3], cs_real_t dfext[][3], cs_real_t phydr[], cs_real_t flumas[], cs_real_t flumab[], cs_real_t viscf[], cs_real_t viscb[], cs_real_t dam[], cs_real_t xam[], cs_real_t dpvar[], cs_real_t rhs[]) |
| void | cpthp1 (const int *mode, cs_real_t *eh, cs_real_t *xesp, cs_real_t *f1mc, cs_real_t *f2mc, cs_real_t *tp) |
| void | csinit (const int *irgpar, const int *nrgpar) |
| void | distpr (const int *itypfb, cs_real_t *distpa) |
| void | dvvpst (const int *nummai, const int *numtyp, const int *nvar, const cs_lnum_t *ncelps, const cs_lnum_t *nfbrps, const cs_lnum_t lstcel[], const cs_lnum_t lstfbr[], cs_real_t tracel[], cs_real_t trafbr[]) |
| void | findpt (const cs_lnum_t *ncelet, const cs_lnum_t *ncel, const cs_real_t *xyzcen, const cs_real_t *xx, const cs_real_t *yy, const cs_real_t *zz, cs_lnum_t *node, int *ndrang) |
| void | haltyp (const int *ivoset) |
| void | initi1 (void) |
| int * | cs_atmo_get_auto_flag (void) |
| Return pointer to automatic face bc flag array. More... | |
| int | cs_add_model_field_indexes (int f_id) |
| void | cs_coal_bt2h (cs_lnum_t n_faces, const cs_lnum_t face_ids[], const cs_real_t t[], cs_real_t h[]) |
| Convert temperature to enthalpy at boundary for coal combustion. More... | |
| void | cs_coal_thfieldconv1 (int location_id, const cs_real_t eh[], cs_real_t tp[]) |
| Calculation of the gas temperature Function with the gas enthalpy and concentrations. More... | |
| cs_real_t * | cs_get_b_head_loss (void) |
| Return pointer to boundary head losses array. More... | |
| cs_real_t * | cs_get_cavitation_dgdp_st (void) |
| Return pointer to cavitation "dgdpca" array. More... | |
| cs_real_t * | cs_get_cavitation_gam (void) |
| Return pointer to cavitation "gamcav" array. More... | |
| void | cs_fuel_bt2h (cs_lnum_t n_faces, const cs_lnum_t face_ids[], const cs_real_t t[], cs_real_t h[]) |
| Convert temperature to enthalpy at boundary for fuel combustion. More... | |
| void | cs_fuel_thfieldconv1 (int location_id, const cs_real_t eh[], cs_real_t tp[]) |
| Calculation of the gas temperature Function with the gas enthalpy and concentrations. More... | |
| void | cs_lagr_status (int *model_flag, int *restart_flag, int *frozen_flag) |
| double | cs_tagms_s_metal (void) |
| void | cs_user_1d_wall_thermal (int iappel, int isuit1) |
| void | cs_user_boundary_conditions_setup (cs_domain_t *domain) |
| Set boundary conditions to be applied. More... | |
| void | cs_user_boundary_conditions (int nvar, int icodcl[], int bc_type[], cs_real_t rcodcl[]) |
| User definition of boundary conditions. More... | |
| void | cs_user_extra_operations_initialize (cs_domain_t *domain) |
| Initialize variables. More... | |
| void | cs_user_extra_operations (cs_domain_t *domain) |
| This function is called at the end of each time step. More... | |
| void | cs_user_extra_operations_finalize (cs_domain_t *domain) |
| This function is called at the end of the calculation. More... | |
| void | cs_user_head_losses (const cs_zone_t *zone, cs_real_t cku[][6]) |
| Compute GUI-defined head losses for a given volume zone. More... | |
| void | cs_user_initialization (cs_domain_t *domain) |
| This function is called one time step to initialize problem. More... | |
| void | cs_user_internal_coupling (void) |
| Define internal coupling options. More... | |
| void | cs_user_internal_coupling_add_volumes (cs_mesh_t *mesh) |
| Define volumes as internal coupling zones. More... | |
| void | cs_user_internal_coupling_from_disjoint_meshes (cs_mesh_t *mesh) |
| Define volumesi from separated meshes as internal coupling zones. More... | |
| void | cs_user_physical_properties (cs_domain_t *domain) |
| This function is called each time step to define physical properties. More... | |
| void | cs_user_physical_properties_h_to_t (cs_domain_t *domain, const cs_zone_t *z, bool z_local, const cs_real_t h[restrict], cs_real_t t[restrict]) |
| User definition of enthalpy to temperature conversion. More... | |
| void | cs_user_physical_properties_t_to_h (cs_domain_t *domain, const cs_zone_t *z, bool z_local, const cs_real_t t[restrict], cs_real_t h[restrict]) |
| User definition of temperature to enthalpy conversion. More... | |
| void | cs_user_source_terms (cs_domain_t *domain, int f_id, cs_real_t *st_exp, cs_real_t *st_imp) |
| Additional user-defined source terms for variable equations (momentum, scalars, turbulence...). More... | |
| void | cs_user_porosity (cs_domain_t *domain) |
Compute the porosity (volume factor 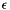 when the porosity model is activated. (cs_glob_porous_model > 0). More... when the porosity model is activated. (cs_glob_porous_model > 0). More... | |
| void | cs_user_join (void) |
| Define mesh joinings. More... | |
| void | cs_user_linear_solvers (void) |
| Define linear solver options. More... | |
| void | cs_user_finalize_setup (cs_domain_t *domain) |
| Define or modify output user parameters. For CDO schemes, specify the elements such as properties, advection fields, user-defined equations and modules which have been previously added. More... | |
| void | cs_user_mesh_bad_cells_tag (cs_mesh_t *mesh, cs_mesh_quantities_t *mesh_quantities) |
| Tag bad cells within the mesh based on user-defined geometric criteria. More... | |
| void | cs_user_mesh_input (void) |
| Define mesh files to read and optional associated transformations. More... | |
| void | cs_user_mesh_modify (cs_mesh_t *mesh) |
| Modify geometry and mesh. More... | |
| void | cs_user_mesh_boundary (cs_mesh_t *mesh) |
| Insert boundaries into a mesh. More... | |
| void | cs_user_mesh_smoothe (cs_mesh_t *mesh) |
| Mesh smoothing. More... | |
| void | cs_user_mesh_save (cs_mesh_t *mesh) |
| Enable or disable mesh saving. More... | |
| void | cs_user_mesh_warping (void) |
| Set options for cutting of warped faces. More... | |
| void | cs_user_mesh_modify_partial (cs_mesh_t *mesh, cs_mesh_quantities_t *mesh_quantities) |
| Apply partial modifications to the mesh after the preprocessing and initial postprocessing mesh building stage. More... | |
| void | cs_user_mesh_cartesian_define (void) |
| Define a cartesian mesh. More... | |
| void | cs_user_model (void) |
| Select physical model options, including user fields. More... | |
| void | cs_user_numbering (void) |
| Define advanced mesh numbering options. More... | |
| void | cs_user_parallel_io (void) |
| Define parallel IO settings. More... | |
| void | cs_user_partition (void) |
| Define advanced partitioning options. More... | |
| void | cs_user_matrix_tuning (void) |
| Define sparse matrix tuning options. More... | |
| void | cs_user_parameters (cs_domain_t *domain) |
| Define or modify general numerical and physical user parameters. More... | |
| void | cs_user_radiative_transfer_parameters (void) |
| User function for input of radiative transfer module options. More... | |
| void | cs_user_radiative_transfer_bcs (int nvar, const int bc_type[], int icodcl[], int isothp[], cs_real_t *tmin, cs_real_t *tmax, cs_real_t *tx, const cs_real_t dt[], cs_real_t rcodcl[], const cs_real_t thwall[], const cs_real_t qincid[], cs_real_t hfcnvp[], cs_real_t flcnvp[], cs_real_t xlamp[], cs_real_t epap[], cs_real_t epsp[], cs_real_t textp[]) |
| User definition of radiative transfer boundary conditions. More... | |
| void | cs_user_periodicity (void) |
| Define periodic faces. More... | |
| void | cs_user_postprocess_writers (void) |
| Define post-processing writers. More... | |
| void | cs_user_postprocess_probes (void) |
| Define monitoring probes and profiles. More... | |
| void | cs_user_postprocess_meshes (void) |
| Define post-processing meshes. More... | |
| void | cs_user_postprocess_values (const char *mesh_name, int mesh_id, int cat_id, cs_probe_set_t *probes, cs_lnum_t n_cells, cs_lnum_t n_i_faces, cs_lnum_t n_b_faces, cs_lnum_t n_vertices, const cs_lnum_t cell_list[], const cs_lnum_t i_face_list[], const cs_lnum_t b_face_list[], const cs_lnum_t vertex_list[], const cs_time_step_t *ts) |
| User function for output of values on a post-processing mesh. More... | |
| void | cs_user_postprocess_activate (int nt_max_abs, int nt_cur_abs, double t_cur_abs) |
| void | cs_user_rad_transfer_absorption (const int bc_type[], cs_real_t ck[]) |
| Absorption coefficient for radiative module. More... | |
| void | cs_user_rad_transfer_net_flux (const int itypfb[], const cs_real_t coefap[], const cs_real_t coefbp[], const cs_real_t cofafp[], const cs_real_t cofbfp[], const cs_real_t twall[], const cs_real_t qincid[], const cs_real_t xlam[], const cs_real_t epa[], const cs_real_t eps[], const cs_real_t ck[], cs_real_t net_flux[]) |
| Compute the net radiation flux. More... | |
| int | cs_user_solver_set (void) |
| Set user solver. More... | |
| void | cs_user_solver (const cs_mesh_t *mesh, const cs_mesh_quantities_t *mesh_quantities) |
| Main call to user solver. More... | |
| void | cs_user_saturne_coupling (void) |
| Define couplings with other instances of Code_Saturne. More... | |
| void | cs_user_syrthes_coupling (void) |
| Define couplings with SYRTHES code. More... | |
| void | cs_user_syrthes_coupling_volume_h (int coupling_id, const char *syrthes_name, cs_lnum_t n_elts, const cs_lnum_t elt_ids[], cs_real_t h_vol[]) |
| Compute a volume exchange coefficient for SYRTHES couplings. More... | |
| void | cs_user_time_moments (void) |
| Define time moments. More... | |
| void | cs_user_turbomachinery (void) |
| Define rotor/stator model. More... | |
| void | cs_user_turbomachinery_rotor (void) |
| Define rotor axes, associated cells, and rotor/stator faces. More... | |
| void | cs_user_turbomachinery_set_rotation_velocity (void) |
| Define rotation velocity of rotor. More... | |
| void | cs_user_zones (void) |
| Define volume and surface zones. More... | |
| void | cs_user_scaling_elec (const cs_mesh_t *mesh, const cs_mesh_quantities_t *mesh_quantities, cs_real_t *dt) |
| Define scaling parameter for electric model. More... | |
| void | cs_user_hgn_thermo_relax_time (const cs_mesh_t *mesh, const cs_real_t *alpha_eq, const cs_real_t *y_eq, const cs_real_t *z_eq, const cs_real_t *ei, const cs_real_t *v, cs_real_t *relax_tau) |
| Computation of the relaxation time-scale. More... | |
| cs_real_t * | cs_meg_boundary_function (const cs_zone_t *zone, const char *field_name, const char *condition) |
| void | cs_meg_volume_function (const cs_zone_t *zone, cs_field_t *f[]) |
| This function is used to compute user defined values for fields over a given volume zone. More... | |
| cs_real_t * | cs_meg_initialization (const cs_zone_t *zone, const char *field_name) |
| Evaluate GUI defined mathematical expressions over volume zones for initialization. More... | |
| cs_real_t * | cs_meg_source_terms (const cs_zone_t *zone, const char *name, const char *source_type) |
| void | cs_meg_immersed_boundaries_inout (int *ipenal, const char *object_name, cs_real_t xyz[3], cs_real_t t) |
| void | cs_meg_fsi_struct (const char *object_type, const char *name, const cs_real_t fluid_f[], cs_real_t val[]) |
| This function is used to query FSI internal coupling structure values for a given boundary and structure. More... | |
| void | cs_meg_post_activate (void) |
| This function is used to activate postprocessing writers. More... | |
| void | cs_meg_post_profiles (const char *name, int n_coords, cs_real_t coords[][3]) |
| This function is used to define profile coordinates. More... | |
| void | cs_user_paramedmem_define_couplings (void) |
| Define ParaMEDMEM coupling(s) More... | |
| void | cs_user_paramedmem_define_meshes (void) |
| Define coupled meshes. More... | |
| void | cs_user_paramedmem_define_fields (void) |
| Define fields to couple with ParaMEDMEM. More... | |
| void caltri | ( | void | ) |
| void cpthp1 | ( | const int * | mode, |
| cs_real_t * | eh, | ||
| cs_real_t * | xesp, | ||
| cs_real_t * | f1mc, | ||
| cs_real_t * | f2mc, | ||
| cs_real_t * | tp | ||
| ) |
| int cs_add_model_field_indexes | ( | int | f_id | ) |
| int* cs_atmo_get_auto_flag | ( | void | ) |
Return pointer to automatic face bc flag array.
| void cs_coal_bt2h | ( | cs_lnum_t | n_faces, |
| const cs_lnum_t | face_ids[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | t[], | ||
| cs_real_t | h[] | ||
| ) |
Convert temperature to enthalpy at boundary for coal combustion.
| [in] | n_faces | number of faces in list |
| [in] | face_ids | list of boundary faces at which conversion is requested (0-based numbering) |
| [in] | t_b | temperature at boundary |
| [out] | h_b | enthalpy at boundary |
Calculation of the gas temperature Function with the gas enthalpy and concentrations.
| [in] | location_id | mesh location id (cells or boundary faces) |
| [in] | eh | gas enthalpy ( 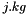 of gaseous mixture) of gaseous mixture) |
| [in,out] | tp | gas temperature (in kelvin) |
| void cs_fuel_bt2h | ( | cs_lnum_t | n_faces, |
| const cs_lnum_t | face_ids[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | t[], | ||
| cs_real_t | h[] | ||
| ) |
Convert temperature to enthalpy at boundary for fuel combustion.
| [in] | n_faces | number of faces in list |
| [in] | face_ids | list of boundary faces at which conversion is requested (0-based numbering) |
| [in] | t_b | temperature at boundary |
| [out] | h_b | enthalpy at boundary |
Calculation of the gas temperature Function with the gas enthalpy and concentrations.
| [in] | location_id | mesh location id (cells or boundary faces) |
| [in] | eh | gas enthalpy ( 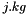 of gaseous mixture) of gaseous mixture) |
| [in,out] | tp | gas temperature (in kelvin) |
| cs_real_t* cs_get_b_head_loss | ( | void | ) |
Return pointer to boundary head losses array.
Return pointer to boundary head losses array.
| cs_real_t* cs_get_cavitation_dgdp_st | ( | void | ) |
Return pointer to cavitation "dgdpca" array.
Return pointer to cavitation "dgdpca" array.
| cs_real_t* cs_get_cavitation_gam | ( | void | ) |
Return pointer to cavitation "gamcav" array.
Return pointer to cavitation "gamcav" array.
| void cs_hydrostatic_pressure_compute | ( | int * | indhyd, |
| int | iterns, | ||
| cs_real_t | fext[][3], | ||
| cs_real_t | dfext[][3], | ||
| cs_real_t | phydr[], | ||
| cs_real_t | flumas[], | ||
| cs_real_t | flumab[], | ||
| cs_real_t | viscf[], | ||
| cs_real_t | viscb[], | ||
| cs_real_t | dam[], | ||
| cs_real_t | xam[], | ||
| cs_real_t | dpvar[], | ||
| cs_real_t | rhs[] | ||
| ) |
| void cs_lagr_status | ( | int * | model_flag, |
| int * | restart_flag, | ||
| int * | frozen_flag | ||
| ) |
| cs_real_t* cs_meg_boundary_function | ( | const cs_zone_t * | zone, |
| const char * | field_name, | ||
| const char * | condition | ||
| ) |
| void cs_meg_fsi_struct | ( | const char * | object_type, |
| const char * | name, | ||
| const cs_real_t | fluid_f[], | ||
| cs_real_t | val[] | ||
| ) |
This function is used to query FSI internal coupling structure values for a given boundary and structure.
| [in] | object_type | name of object type |
| [in] | name | name of matching boundary |
| [in] | fluid_f | array of fluid forces on the object |
| [in,out] | val[] | matrix or vector coefficients |
| [in] | object_type | name of object type |
| [in] | name | name of matching boundary |
| [in] | fluid_f | array of fluid forces on the object |
| [in,out] | val[] | matrix or vector coefficients |
| void cs_meg_immersed_boundaries_inout | ( | int * | ipenal, |
| const char * | object_name, | ||
| cs_real_t | xyz[3], | ||
| cs_real_t | t | ||
| ) |
Evaluate GUI defined mathematical expressions over volume zones for initialization.
| [in] | zone | pointer to a cs_volume_zone_t structure |
| [in] | field_name | variable name |
Evaluate GUI defined mathematical expressions over volume zones for initialization.
The caller is responsible for freeing the associated array.
| [in] | zone | pointer to associated volume zone |
| [in,out] | field_name | associated field name |
| void cs_meg_post_activate | ( | void | ) |
This function is used to activate postprocessing writers.
| void cs_meg_post_profiles | ( | const char * | name, |
| int | n_coords, | ||
| cs_real_t | coords[][3] | ||
| ) |
This function is used to define profile coordinates.
| [in] | name | name of matching profile |
| [in] | n_coords | number of point coordinates |
| [in,out] | coords | point coordinates |
| cs_real_t* cs_meg_source_terms | ( | const cs_zone_t * | zone, |
| const char * | name, | ||
| const char * | source_type | ||
| ) |
| void cs_meg_volume_function | ( | const cs_zone_t * | zone, |
| cs_field_t * | f[] | ||
| ) |
This function is used to compute user defined values for fields over a given volume zone.
| [in] | zone | pointer to cs_zone_t structure related to a volume |
| [in,out] | f[] | array of pointers to cs_field_t |
| double cs_tagms_s_metal | ( | void | ) |
| void cs_user_1d_wall_thermal | ( | int | iappel, |
| int | isuit1 | ||
| ) |
| void cs_user_boundary_conditions | ( | int | nvar, |
| int | bc_type[], | ||
| int | icodcl[], | ||
| cs_real_t | rcodcl[] | ||
| ) |
User definition of boundary conditions.
| [in] | nvar | total number of variable BC's |
| [in] | bc_type | boundary face types |
| [in] | icodcl | boundary face code
|
| [in] | rcodcl | boundary condition values rcodcl(3) = flux density value (negative for gain) in W/m2 |
| void cs_user_boundary_conditions_setup | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain | ) |
Set boundary conditions to be applied.
This function is called just before cs_user_finalize_setup, and boundary conditions can be defined in either of those functions, depending on whichever is considered more readable or practical for a given use.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| void cs_user_extra_operations | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain | ) |
This function is called at the end of each time step.
It has a very general purpose, although it is recommended to handle mainly postprocessing or data-extraction type operations.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| void cs_user_extra_operations_finalize | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain | ) |
This function is called at the end of the calculation.
It has a very general purpose, although it is recommended to handle mainly postprocessing or data-extraction type operations.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| void cs_user_extra_operations_initialize | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain | ) |
Initialize variables.
This function is called at beginning of the computation (restart or not) before the time step loop.
This is intended to initialize or modify (when restarted) variable and time step values.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| void cs_user_finalize_setup | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain | ) |
Define or modify output user parameters. For CDO schemes, specify the elements such as properties, advection fields, user-defined equations and modules which have been previously added.
Define or modify output user parameters. For CDO schemes, specify the elements such as properties, advection fields, user-defined equations and modules which have been previously added.
For CDO schemes, this function concludes the setup of properties, equations, source terms...
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
Compute GUI-defined head losses for a given volume zone.
Head loss tensor coefficients for each cell are organized as follows: cku11, cku22, cku33, cku12, cku13, cku23.
| [in] | zone | pointer to zone structure |
| [in,out] | cku | head loss coefficients |
Compute GUI-defined head losses for a given volume zone.
Head loss tensor coefficients for each cell are organized as follows: ck11, ck22, ck33, ck12, ck13, ck23.
Coefficients are set to zero (then computed based on definitions provided through the GUI if this is the case) before calling this function, so setting values to zero is usually not necessary, unless we want to fully overwrite a GUI-based definition.
Diagonal coefficients must be positive; the calculation may diverge if this is not the case.
| [in] | zone | pointer to zone structure |
| [in,out] | cku | head loss coefficients |
| void cs_user_hgn_thermo_relax_time | ( | const cs_mesh_t * | mesh, |
| const cs_real_t * | alpha_eq, | ||
| const cs_real_t * | y_eq, | ||
| const cs_real_t * | z_eq, | ||
| const cs_real_t * | ei, | ||
| const cs_real_t * | v, | ||
| cs_real_t * | relax_tau | ||
| ) |
Computation of the relaxation time-scale.
This function computes the value of the relaxation time-scale (for the return to equilibrium).
| [in] | mesh | pointer to mesh |
| [in] | alpha_eq | equilibrium volume fraction |
| [in] | y_eq | equilibrium mass fraction |
| [in] | z_eq | equilibrium energy fraction |
| [in] | ei | specific internal energy |
| [in] | v | specific volume |
| [in] | relax_tau | relaxation time scale towards equilibrium |
| void cs_user_initialization | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain | ) |
This function is called one time step to initialize problem.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| void cs_user_internal_coupling | ( | void | ) |
Define internal coupling options.
Options are usually defined using cs_internal_coupling_add_entity.
| void cs_user_internal_coupling_add_volumes | ( | cs_mesh_t * | mesh | ) |
Define volumes as internal coupling zones.
These zones will be separated from the rest of the domain using automatically defined thin walls.
| [in,out] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
These zones will be separated from the rest of the domain using automatically defined thin walls.
| [in,out] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
| void cs_user_internal_coupling_from_disjoint_meshes | ( | cs_mesh_t * | mesh | ) |
Define volumesi from separated meshes as internal coupling zones.
These zones must be disjoint and the face selection criteria must be specified.
| [in,out] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
Define volumesi from separated meshes as internal coupling zones.
These zones must be disjoint and the face selection criteria must be specified.
| [in,out] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
| void cs_user_join | ( | void | ) |
Define mesh joinings.
| void cs_user_linear_solvers | ( | void | ) |
Define linear solver options.
This function is called at the setup stage, once user and most model-based fields are defined.
Available native iterative linear solvers include conjugate gradient, Jacobi, BiCGStab, BiCGStab2, and GMRES. For symmetric linear systems, an algebraic multigrid solver is available (and recommended).
External solvers may also be setup using this function, the cs_sles_t mechanism allowing such through user-define functions.
| void cs_user_matrix_tuning | ( | void | ) |
Define sparse matrix tuning options.
| void cs_user_mesh_bad_cells_tag | ( | cs_mesh_t * | mesh, |
| cs_mesh_quantities_t * | mesh_quantities | ||
| ) |
Tag bad cells within the mesh based on user-defined geometric criteria.
| [in,out] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
| [in,out] | mesh_quantities | pointer to a cs_mesh_quantities_t structure |
| void cs_user_mesh_boundary | ( | cs_mesh_t * | mesh | ) |
Insert boundaries into a mesh.
| [in,out] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
| void cs_user_mesh_cartesian_define | ( | void | ) |
Define a cartesian mesh.
| void cs_user_mesh_input | ( | void | ) |
Define mesh files to read and optional associated transformations.
| void cs_user_mesh_modify | ( | cs_mesh_t * | mesh | ) |
Modify geometry and mesh.
| [in,out] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
| void cs_user_mesh_modify_partial | ( | cs_mesh_t * | mesh, |
| cs_mesh_quantities_t * | mesh_quantities | ||
| ) |
Apply partial modifications to the mesh after the preprocessing and initial postprocessing mesh building stage.
| [in,out] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
| [in,out] | mesh_quantities | pointer to a cs_mesh_quantities_t structure |
| void cs_user_mesh_save | ( | cs_mesh_t * | mesh | ) |
Enable or disable mesh saving.
By default, mesh is saved when modified.
| [in,out] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
| void cs_user_mesh_smoothe | ( | cs_mesh_t * | mesh | ) |
Mesh smoothing.
| [in,out] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
| void cs_user_mesh_warping | ( | void | ) |
Set options for cutting of warped faces.
| void cs_user_model | ( | void | ) |
Select physical model options, including user fields.
This function is called at the earliest stages of the data setup, so field ids are not available yet.
| void cs_user_numbering | ( | void | ) |
Define advanced mesh numbering options.
| void cs_user_parallel_io | ( | void | ) |
Define parallel IO settings.
| void cs_user_paramedmem_define_couplings | ( | void | ) |
Define ParaMEDMEM coupling(s)
| void cs_user_paramedmem_define_fields | ( | void | ) |
Define fields to couple with ParaMEDMEM.
| void cs_user_paramedmem_define_meshes | ( | void | ) |
Define coupled meshes.
| void cs_user_parameters | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain | ) |
Define or modify general numerical and physical user parameters.
At the calling point of this function, most model-related most variables and other fields have been defined, so specific settings related to those fields may be set here.
At this stage, the mesh is not built or read yet, so associated data such as field values are not accessible yet, though pending mesh operations and some fields may have been defined.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| void cs_user_partition | ( | void | ) |
Define advanced partitioning options.
| void cs_user_periodicity | ( | void | ) |
Define periodic faces.
| void cs_user_physical_properties | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain | ) |
This function is called each time step to define physical properties.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
This function is called each time step to define physical properties.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| void cs_user_physical_properties_h_to_t | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain, |
| const cs_zone_t * | z, | ||
| bool | z_local, | ||
| const cs_real_t | h[restrict], | ||
| cs_real_t | t[restrict] | ||
| ) |
User definition of enthalpy to temperature conversion.
This allows overwriting the solver defaults if necessary.
This function may be called on a per-zone basis, so as to allow different conversion relations in zones representing solids or different fluids.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| [in] | z | zone (volume or boundary) applying to current call |
| [in] | z_local | if true, h and t arrays are defined in a compact (contiguous) manner for this zone only; if false, h and t are defined on the zone's parent location (usually all cells or boundary faces) |
| [in] | h | enthalpy values |
| [in,out] | t | temperature values |
| void cs_user_physical_properties_t_to_h | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain, |
| const cs_zone_t * | z, | ||
| bool | z_local, | ||
| const cs_real_t | t[restrict], | ||
| cs_real_t | h[restrict] | ||
| ) |
User definition of temperature to enthalpy conversion.
This allows overwriting the solver defaults if necessary.
This function may be called on a per-zone basis, so as to allow different conversion relations in zones representing solids or different fluids.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| [in] | z | zone (volume or boundary) applying to current call |
| [in] | z_local | if true, h and t arrays are defined in a compact (contiguous) manner for this zone only; if false, h and t are defined on the zone's parent location (usually all cells or boundary faces) |
| [in] | h | temperature values |
| [in,out] | t | enthalpy values |
| void cs_user_porosity | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain | ) |
Compute the porosity (volume factor 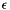 when the porosity model is activated. (cs_glob_porous_model > 0).
when the porosity model is activated. (cs_glob_porous_model > 0).
This function is called at the begin of the simulation only.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
Compute the porosity (volume factor 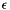 when the porosity model is activated. (cs_glob_porous_model > 0).
when the porosity model is activated. (cs_glob_porous_model > 0).
This function is called at the begin of the simulation only.
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| void cs_user_postprocess_activate | ( | int | nt_max_abs, |
| int | nt_cur_abs, | ||
| double | t_cur_abs | ||
| ) |
Override default frequency or calculation end based output.
This allows fine-grained control of activation or deactivation,
| [in] | nt_max_abs | maximum time step number |
| [in] | nt_cur_abs | current time step number |
| [in] | t_cur_abs | absolute time at the current time step |
| void cs_user_postprocess_meshes | ( | void | ) |
Define post-processing meshes.
The main post-processing meshes may be configured, and additional post-processing meshes may be defined as a subset of the main mesh's cells or faces (both interior and boundary).
| void cs_user_postprocess_probes | ( | void | ) |
Define monitoring probes and profiles.
Profiles are defined as sets of probes.
| void cs_user_postprocess_values | ( | const char * | mesh_name, |
| int | mesh_id, | ||
| int | cat_id, | ||
| cs_probe_set_t * | probes, | ||
| cs_lnum_t | n_cells, | ||
| cs_lnum_t | n_i_faces, | ||
| cs_lnum_t | n_b_faces, | ||
| cs_lnum_t | n_vertices, | ||
| const cs_lnum_t | cell_list[], | ||
| const cs_lnum_t | i_face_list[], | ||
| const cs_lnum_t | b_face_list[], | ||
| const cs_lnum_t | vertex_list[], | ||
| const cs_time_step_t * | ts | ||
| ) |
User function for output of values on a post-processing mesh.
| [in] | mesh_name | name of the output mesh for the current call |
| [in] | mesh_id | id of the output mesh for the current call |
| [in] | cat_id | category id of the output mesh for the current call |
| [in] | probes | pointer to associated probe set structure if the mesh is a probe set, NULL otherwise |
| [in] | n_cells | local number of cells of post_mesh |
| [in] | n_i_faces | local number of interior faces of post_mesh |
| [in] | n_b_faces | local number of boundary faces of post_mesh |
| [in] | n_vertices | local number of vertices faces of post_mesh |
| [in] | cell_list | list of cells (0 to n-1) of post-processing mesh |
| [in] | i_face_list | list of interior faces (0 to n-1) of post-processing mesh |
| [in] | b_face_list | list of boundary faces (0 to n-1) of post-processing mesh |
| [in] | vertex_list | list of vertices (0 to n-1) of post-processing mesh |
| [in] | ts | time step status structure, or NULL |
| void cs_user_postprocess_writers | ( | void | ) |
Define post-processing writers.
The default output format and frequency may be configured, and additional post-processing writers allowing outputs in different formats or with different format options and output frequency than the main writer may be defined.
| void cs_user_rad_transfer_absorption | ( | const int | bc_type[], |
| cs_real_t | ck[] | ||
| ) |
Absorption coefficient for radiative module.
It is necessary to define the value of the fluid's absorption coefficient Ck.
This value is defined automatically for specific physical models, such as gas and coal combustion, so this function is not used by these models.
For a transparent medium, the coefficient should be set to 0.
In the case of the P-1 model, we check that the optical length is at least of the order of 1.
| [in] | bc_type | boundary face types |
| [out] | ck | medium's absorption coefficient (zero if transparent) |
| void cs_user_rad_transfer_net_flux | ( | const int | bc_type[], |
| const cs_real_t | coefap[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | coefbp[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | cofafp[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | cofbfp[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | twall[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | qincid[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | xlam[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | epa[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | eps[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | ck[], | ||
| cs_real_t | net_flux[] | ||
| ) |
Compute the net radiation flux.
The density of net radiation flux must be calculated consistently with the boundary conditions of the intensity. The density of net flux is the balance between the radiative emiting part of a boundary face (and not the reflecting one) and the radiative absorbing part.
| [in] | bc_type | boundary face types |
| [in] | coefap | boundary condition work array for the luminance (explicit part) |
| [in] | coefbp | boundary condition work array for the luminance (implicit part) |
| [in] | cofafp | boundary condition work array for the diffusion of the luminance (explicit part) |
| [in] | cofbfp | boundary condition work array for the diffusion of the luminance (implicit part) |
| [in] | twall | inside current wall temperature (K) |
| [in] | qincid | radiative incident flux (W/m2) |
| [in] | xlam | conductivity (W/m/K) |
| [in] | epa | thickness (m) |
| [in] | eps | emissivity (>0) |
| [in] | ck | absorption coefficient |
| [out] | net_flux | net flux (W/m2) |
| void cs_user_radiative_transfer_bcs | ( | int | nvar, |
| const int | bc_type[], | ||
| int | icodcl[], | ||
| int | isothp[], | ||
| cs_real_t * | tmin, | ||
| cs_real_t * | tmax, | ||
| cs_real_t * | tx, | ||
| const cs_real_t | dt[], | ||
| cs_real_t | rcodcl[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | thwall[], | ||
| const cs_real_t | qincid[], | ||
| cs_real_t | hfcnvp[], | ||
| cs_real_t | flcnvp[], | ||
| cs_real_t | xlamp[], | ||
| cs_real_t | epap[], | ||
| cs_real_t | epsp[], | ||
| cs_real_t | textp[] | ||
| ) |
User definition of radiative transfer boundary conditions.
See Examples of data settings for radiative transfers for examples.
For each boundary face face_id, a specific output (logging and postprocessing) class id may be assigned. This allows realizing balance sheets by treating them separately for each zone. By default, the output class id is set to the general (input) zone id associated to a face.
To access output class ids (both for reading and modifying), use the cs_boundary_zone_face_class_id function. The zone id values are arbitrarily chosen by the user, but must be positive integers; very high numbers may also lead to higher memory consumption.
The following face characteristics must be set:
Depending on the value of isothp, other values may also need to be set:
| [in] | nvar | total number of variable BC's |
| [in] | bc_type | boundary face types |
| [in] | icodcl | boundary face code |
| [in] | isothp | boundary face type for radiative transfer |
| [out] | tmin | min allowed value of the wall temperature |
| [out] | tmax | max allowed value of the wall temperature |
| [in] | tx | relaxation coefficient (0 < tx < 1) |
| [in] | dt | time step (per cell) |
| [in] | rcodcl | boundary condition values rcodcl(3) = flux density value (negative for gain) in W/m2 |
| [in] | thwall | inside current wall temperature (K) |
| [in] | qincid | radiative incident flux (W/m2) |
| [in] | hfcnvp | convective exchange coefficient (W/m2/K) |
| [in] | flcnvp | convective flux (W/m2) |
| [out] | xlamp | conductivity (W/m/K) |
| [out] | epap | thickness (m) |
| [out] | epsp | emissivity (>0) |
| [out] | textp | outside temperature (K) |
| void cs_user_radiative_transfer_parameters | ( | void | ) |
User function for input of radiative transfer module options.
| void cs_user_saturne_coupling | ( | void | ) |
Define couplings with other instances of Code_Saturne.
This is done by calling the cs_sat_coupling_define function for each coupling to add.
| void cs_user_scaling_elec | ( | const cs_mesh_t * | mesh, |
| const cs_mesh_quantities_t * | mesh_quantities, | ||
| cs_real_t * | dt | ||
| ) |
Define scaling parameter for electric model.
Define scaling parameter for electric model.
| [in] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
| [in,out] | mesh_quantities | pointer to a cs_mesh_quantities_t structure |
| [in] | dt | pointer to a cs_real_t |
These options allow defining the time step synchronization policy, as well as a time step multiplier.
| void cs_user_solver | ( | const cs_mesh_t * | mesh, |
| const cs_mesh_quantities_t * | mesh_quantities | ||
| ) |
Main call to user solver.
| [in] | mesh | pointer to a cs_mesh_t structure |
| [in,out] | mesh_quantities | pointer to a cs_mesh_quantities_t structure |
| int cs_user_solver_set | ( | void | ) |
Set user solver.
| void cs_user_source_terms | ( | cs_domain_t * | domain, |
| int | f_id, | ||
| cs_real_t * | st_exp, | ||
| cs_real_t * | st_imp | ||
| ) |
Additional user-defined source terms for variable equations (momentum, scalars, turbulence...).
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| [in] | f_id | field id of the variable |
| [out] | st_exp | explicit source term |
| [out] | st_imp | implicit part of the source term |
This function is called at each time step, for each relevant field. It is therefore necessary to test the value of the field id or name to separate the treatments of the different variables.
The additional source term is decomposed into an explicit part (st_exp) and an implicit part (st_imp) that must be provided here. The resulting equation solved by the code for a scalar f is:
![\[ \rho*volume*\frac{df}{dt} + .... = st\_imp*f + st\_exp \]](form_643.png)
Note that st_exp and st_imp are defined after the Finite Volume integration over the cells, so they include the "volume" term. More precisely:
The st_exp and st_imp arrays are already initialized to 0 (or a value defined through the GUI or defined by a model) before entering the function. It is generally not useful to reset them here.
For stability reasons, Code_Saturne will not add -st_imp directly to the diagonal of the matrix, but Max(-st_imp,0). This way, the st_imp term is treated implicitely only if it strengthens the diagonal of the matrix. However, when using the second-order in time scheme, this limitation cannot be done anymore and -st_imp is added directly. The user should therefore check for the negativity of st_imp.
When using the second-order in time scheme, one should supply:
If the variable is a temperature, the resulting equation solved is:
rho*Cp*volume*dT/dt + .... = st_imp*T + st_exp
Note that st_exp and st_imp are defined after the Finite Volume integration over the cells, so they include the "volume" term. More precisely:
In case of a complex, non-linear source term, say F(f), for variable f, the easiest method is to implement the source term explicitly.
df/dt = .... + F(f(n)) where f(n) is the value of f at time tn, the beginning of the time step.
This yields: st_exp = volume*F(f(n)) st_imp = 0
However, if the source term is potentially steep, this fully explicit method will probably generate instabilities. It is therefore wiser to partially implicit the term by writing:
df/dt = .... + dF/df*f(n+1) - dF/df*f(n) + F(f(n))
This yields: st_exp = volume*( F(f(n)) - dF/df*f(n) ) st_imp = volume*dF/df
| [in,out] | domain | pointer to a cs_domain_t structure |
| [in] | f_id | field id of the variable |
| [out] | st_exp | explicit source term |
| [out] | st_imp | implicit part of the source term |
| void cs_user_syrthes_coupling | ( | void | ) |
Define couplings with SYRTHES code.
This is done by calling the cs_syr_coupling_define function for each coupling to add.
| void cs_user_syrthes_coupling_volume_h | ( | int | coupling_id, |
| const char * | syrthes_name, | ||
| cs_lnum_t | n_elts, | ||
| const cs_lnum_t | elt_ids[], | ||
| cs_real_t | h_vol[] | ||
| ) |
Compute a volume exchange coefficient for SYRTHES couplings.
| [in] | coupling_id | Syrthes coupling id |
| [in] | syrthes_name | name of associated Syrthes instance |
| [in] | n_elts | number of associated cells |
| [in] | elt_ids | associated cell ids |
| [out] | h_vol | associated exchange coefficient (size: n_elts) |
| void cs_user_time_moments | ( | void | ) |
Define time moments.
This function is called at the setup stage, once user and most model-based fields are defined, and before fine control of field output options is defined.
| void cs_user_turbomachinery | ( | void | ) |
Define rotor/stator model.
| void cs_user_turbomachinery_rotor | ( | void | ) |
Define rotor axes, associated cells, and rotor/stator faces.
| void cs_user_turbomachinery_set_rotation_velocity | ( | void | ) |
Define rotation velocity of rotor.
| void cs_user_zones | ( | void | ) |
Define volume and surface zones.
See Element selection criteria for details on selection criteria.
| void csinit | ( | const int * | irgpar, |
| const int * | nrgpar | ||
| ) |
| void distpr | ( | const int * | itypfb, |
| cs_real_t * | distpa | ||
| ) |
| void dvvpst | ( | const int * | nummai, |
| const int * | numtyp, | ||
| const int * | nvar, | ||
| const cs_lnum_t * | ncelps, | ||
| const cs_lnum_t * | nfbrps, | ||
| const cs_lnum_t | lstcel[], | ||
| const cs_lnum_t | lstfbr[], | ||
| cs_real_t | tracel[], | ||
| cs_real_t | trafbr[] | ||
| ) |
| void findpt | ( | const cs_lnum_t * | ncelet, |
| const cs_lnum_t * | ncel, | ||
| const cs_real_t * | xyzcen, | ||
| const cs_real_t * | xx, | ||
| const cs_real_t * | yy, | ||
| const cs_real_t * | zz, | ||
| cs_lnum_t * | node, | ||
| int * | ndrang | ||
| ) |
| void haltyp | ( | const int * | ivoset | ) |
| void initi1 | ( | void | ) |