Additional right-hand side source terms for velocity components equation (Navier-Stokes)
Local variables and initialization
const cs_lnum_t n_cells = domain->mesh->n_cells;
double cs_real_t
Floating-point value.
Definition: cs_defs.h:342
int cs_lnum_t
local mesh entity id
Definition: cs_defs.h:335
cs_field_t * cs_field_by_id(int id)
Return a pointer to a field based on its id.
Definition: cs_field.cpp:2465
@ rho
Definition: cs_field_pointer.h:99
#define CS_F_(e)
Macro used to return a field pointer by its enumerated value.
Definition: cs_field_pointer.h:51
double precision, dimension(:), pointer cell_f_vol
fluid volume of each cell
Definition: mesh.f90:104
Field descriptor.
Definition: cs_field.h:131
Example
Example of arbitrary source term for component 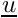 :
:
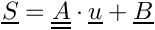 appearing in the equation under the form:
appearing in the equation under the form:
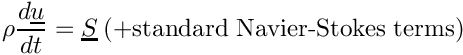
In the following example:
![\[ \tens{A} = -\rho \cdot \tens{CKP} \]](form_751.png)
![\[ \vect{B} = \vect{XMMT} \]](form_752.png)
with:
CKP = 1.0 (in 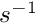 ) (return term on velocity)
) (return term on velocity)
MMT = 100.0 (in 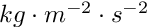 ) (momentum production by volume and time unit)
) (momentum production by volume and time unit)
which yields:
st_imp[i][0][0] = volume[i] * A = - volume[i]*(rho*CKP)
st_exp[i][0] = volume[i] * B = volume[i]*(XMMT)
Body
_st_imp[i][0][0] = -
cell_f_vol[i] * cpro_rom[i] * ckp;
}
}
cs_real_t cs_real_3_t[3]
vector of 3 floating-point values
Definition: cs_defs.h:359
cs_real_t cs_real_33_t[3][3]
3x3 matrix of floating-point values
Definition: cs_defs.h:368
@ vel
Definition: cs_field_pointer.h:70
Example of a boussinesq momentum source term
Example to add Boussinesq source to the z component of 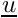 :
:
Body
}
}
@ t
Definition: cs_field_pointer.h:94
const cs_fluid_properties_t * cs_glob_fluid_properties
Definition: cs_physical_constants.cpp:465
real(c_double), pointer, save t0
reference temperature.
Definition: cstphy.f90:217
real(c_double), pointer, save ro0
reference density.
Definition: cstphy.f90:153
double ro0
Definition: cs_physical_constants.h:74
double t0
Definition: cs_physical_constants.h:82
![]() :
:![]() appearing in the equation under the form:
appearing in the equation under the form:![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() :
: