Activation of the module
The module can be activated in the usppmo routine in cs_user_parameters.f90. The corresponding keyword is iirayo in the cs_glob_rad_transfer_params structure.
This member can take the values:
- iirayo = 0: module desactivated.
- iirayo = 1: the module is activated and the Discrete Ordinates Method is used.
- iirayo = 2: the module is activated and the P1 model is used.
Radiation module specific parameters.
When the module is activated, its specific input parameters should be set in the cs_user_radiative_transfer_parameters function of the cs_user_radiative_transfer.c file.
Calculation options for the radiative transfer module.
Radiative transfer parameters may be defined using the cs_user_radiative_transfer_parameters function.
- 1,
-1,
5,
true,
false);
cs_rad_transfer_params_t * cs_glob_rad_transfer_params
@ CS_RAD_ATMO_3D_DIFFUSE_SOLAR
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:115
@ CS_RAD_ATMO_3D_DIFFUSE_SOLAR_O3BAND
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:116
@ CS_RAD_ATMO_3D_INFRARED
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:118
@ CS_RAD_ATMO_3D_DIRECT_SOLAR
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:112
@ CS_RAD_ATMO_3D_DIRECT_SOLAR_O3BAND
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:113
int cs_restart_present(void)
Check if we have a restart directory.
Definition: cs_restart.c:2097
void cs_time_control_init_by_time_step(cs_time_control_t *tc, int nt_start, int nt_end, int nt_interval, bool at_start, bool at_end)
Definition: cs_time_control.c:232
int restart
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:161
int imfsck
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:147
int i_quadrature
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:156
int idiver
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:149
int imodak
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:139
int iimpar
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:137
cs_time_control_t time_control
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:207
int atmo_model
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:172
int verbosity
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:138
int ndirec
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:157
int imoadf
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:142
Radiative transfer boundary conditions
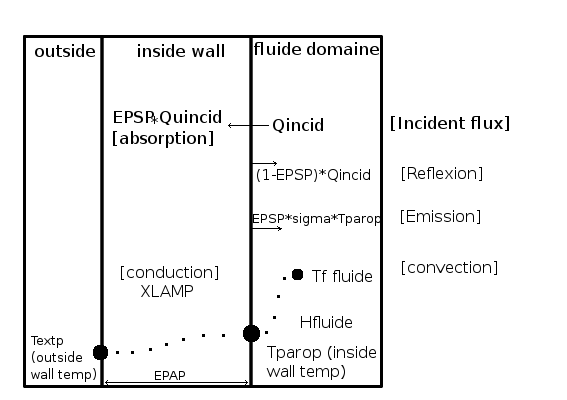
Sketch of thermal flux in boundary walls
The radiative boundary condition is based on the calculation of a new wall temperature. This temperature is computed with a thermal flux balance:
![\[{ Q_{conduction} = Q_{convection} + (Q_{rayt_{absorption}} - Q_{rayt_{emission}}}) \]](form_732.png)
Therefore :
![\[ \dfrac{xlamp}{epap} (T_{fluid} - T_{wall}) = h_{fluid} (T_{fluid} - T_{wall}) + epsp (Q_{incid} - \sigma * T_{wall}) \]](form_733.png)
- Note
- In
code_saturne the flux is positive when it is oriented from inside to outside.
| Body | Emissivity |
| polished steel | 0.06 |
| oxidized steel | 0.80 |
| steel rough | 0.94 |
| polished aluminium | 0.04 |
| oxidiezd aluminium (inside) | 0.09 |
| oxidized aluminium (wet air) | 0.90 |
| brick | 0.93 |
| concrete | 0.93 |
| paper | 0.8 to 0.9 |
| water | 0.96 |
Boundary faces identification
Boundary faces may be identified using the getfbr function, or preferrably, through boundary zones, defined using the GUI or the cs_user_zones function..
Initialization and finalization
The following declaration and initialization block needs to be added for the following examples:
int * cs_boundary_zone_face_class_id(void)
Get pointer to optional boundary face class ids.
Definition: cs_boundary_zone.c:1026
double cs_real_t
Floating-point value.
Definition: cs_defs.h:319
const double cs_physical_constants_celsius_to_kelvin
Definition: cs_physical_constants.c:408
double precision tkelvi
Temperature in Kelvin correponding to 0 degrees Celsius (= +273,15)
Definition: cstphy.f90:44
Remaining initialization
ivar: number of the thermal variable
cs_field_t * cs_thermal_model_field(void)
Definition: cs_thermal_model.c:216
Field descriptor.
Definition: cs_field.h:131
Min and Max values for the wall temperatures (clipping otherwise)
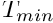 and
and 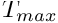 are given in Kelvin.
are given in Kelvin.
*tmin = 0.0;
const cs_real_t cs_math_big_r
Assign boundary conditions to boundary wall
Zone definitions
For each boundary face face_id, a specific output (logging and postprocessing) zone id may be assigned. This allows realizing balance sheets by treating them separately for each zone. By default, the output zone id is set to the general (input) zone id associated to a face.
To access output zone ids (both for reading and modifying), use the cs_boundary_zone_face_zone_id function.
Wall characteristics
- Warning
- The unit of the temperature is the Kelvin
Mandatory data
isothp(ifac) boundary face type
CS_BOUNDARY_RAD_WALL_GRAY: Gray wall with temperature based on fluid BCsCS_BOUNDARY_RAD_WALL_GRAY_EXTERIOR_T: Gray wall with fixed exterior temperatureCS_BOUNDARY_RAD_WALL_REFL_EXTERIOR_T: Reflecting wall with fixed outside temperature (same as Gray wall with zero emissivity)CS_BOUNDARY_RAD_WALL_GRAY_COND_FLUX: Gray wall with fixed conduction fluxCS_BOUNDARY_RAD_WALL_GRAY_REFL_FLUX: Reflecting wall with fixed conduction flux
Other data (depending of the isothp)
rcodcl = conduction fluxepsp = emissivityxlamp = conductivity ( 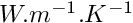 )
)epap = thickness ( 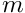 )
)textp = outside temperature ( 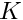 )
)
Examples of boundary conditions
Here is a list of examples:
Gray or black wall with profil of fixed inside temperature
For wall boundary faces, selection criteria: color 1
izfrdp[face_id] = 51;
epsp[face_id] = 0.1;
}
}
const cs_zone_t * cs_boundary_zone_by_name(const char *name)
Return a pointer to a boundary zone based on its name if present.
Definition: cs_boundary_zone.c:711
int cs_lnum_t
local mesh entity id
Definition: cs_defs.h:313
@ CS_SMOOTHWALL
Definition: cs_parameters.h:87
@ CS_BOUNDARY_RAD_WALL_GRAY
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:82
const cs_lnum_t * elt_ids
Definition: cs_zone.h:65
cs_lnum_t n_elts
Definition: cs_zone.h:64
Gray or black wall with fixed outside temperature \f$ T_{ext} \f$
For wall boundary faces, selection criteria: color 2
izfrdp[face_id] = 52;
epsp[face_id] = 0.9;
xlamp[face_id] = 3.0;
epap[face_id] = 0.1;
textp[face_id] = 200. +
tkelvi;
}
}
@ CS_ROUGHWALL
Definition: cs_parameters.h:88
@ CS_BOUNDARY_RAD_WALL_GRAY_EXTERIOR_T
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:89
Reflecting wall (\f$ epsp = 0 \f$) with fixed outside temperature \f$ T_{ext} \f$
For wall boundary faces, selection criteria: color 3
izfrdp[face_id] = 53;
xlamp[face_id] = 3.0;
epap[face_id] = 0.10;
textp[face_id] = 200.0 +
tkelvi;
}
}
@ CS_BOUNDARY_RAD_WALL_REFL_EXTERIOR_T
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:95
Gray or black wall and fixed conduction flux through the wall
For wall boundary faces which have the color 4:
![\[ \begin{array}{rcl} \frac{\texttt{xlamp}}{\texttt{epap}} \cdot (T_{wall} - T_{ext}) &=& \text{fixed conduction flux in } W.m^{-2} \\ &=& \texttt{rodcl(ifac,ivar,3)} \end{array} \]](form_739.png)
If the conduction flux is zero then the wall is adiabatic. The array 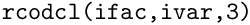 has the value of the flux.
has the value of the flux.
Flux density (< 0 if gain for the fluid)
- For temperature
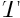 , in
, in 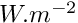 :
:
![\[ rcodcl(ifac,ivar,3)=C_p (viscls+\frac{visct}{\sigma})\cdot \grad{T}\cdot \vect{n} \]](form_743.png)
izfrdp[face_id] = 54;
epsp[face_id] = 0.9;
}
}
@ CS_BOUNDARY_RAD_WALL_GRAY_COND_FLUX
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:99
cs_real_t * rcodcl3
Definition: cs_field.h:111
cs_field_bc_coeffs_t * bc_coeffs
Definition: cs_field.h:163
Reflecting wall and fixed conduction flux through the wall
For wall boundary faces which have the color 5:
![\[ \frac{xlamp}{epap} \cdot (T_{wall} - T_{ext}) = \text{fixed conduction flux} \]](form_747.png)
and 
If the conduction flux is zero then the wall is adiabatic. Flux density (< 0 if gain for the fluid)
izfrdp[face_id] = 55;
}
}
@ CS_BOUNDARY_RAD_WALL_REFL_COND_FLUX
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:103
Absorption coefficient and net radiation flux
The absorption coefficient and the net radiation flux for the radiative module can be defined in cs_user_radiative_transfer.c through the cs_user_rad_transfer_absorption and Net radiation flux subroutines.
Absorption coefficient
The absorption coefficient is defined in cs_user_rad_transfer_absorption.
Computation of the absorption coefficient
ck[cell_id] = 0.;
cs_lnum_t n_cells
Definition: cs_mesh.h:97
Net radiation flux
The net radiation flux is computed in Net radiation flux.
Local variables to be added
const double cs_physical_constants_stephan
Definition: cs_physical_constants.c:413
double precision stephn
Stephan constant for the radiative module in .
Definition: cstphy.f90:53
Initialization
At the end of the subroutine, if iok is different from zero, some faces have been forgotten and the calculation stops.
Computation of the net radiation flux
net_flux[ifac] =
eps[ifac] * (qincid[ifac] -
stephn * pow(twall[ifac], 4));
net_flux[ifac] = 0.0;
net_flux[ifac] = qincid[ifac] -
cs_math_pi * coefap[ifac];
net_flux[ifac] = 0.0;
}
else
(__FILE__, __LINE__, 0,
"In %s:\n"
" non-handled boundary faces for net flux calculation\n\n"
" Last face: %10ld; zone = %d; nature = %d\n",
__func__,
(long)ifac,
bc_type[ifac]);
}
void bft_error(const char *const file_name, const int line_num, const int sys_error_code, const char *const format,...)
Calls the error handler (set by bft_error_handler_set() or default).
Definition: bft_error.c:193
const int * cs_boundary_zone_face_zone_id(void)
Return pointer to zone id associated with each boundary face.
Definition: cs_boundary_zone.c:845
@ eps
Definition: cs_field_pointer.h:71
const cs_real_t cs_math_pi
@ CS_OUTLET
Definition: cs_parameters.h:84
@ CS_INLET
Definition: cs_parameters.h:83
@ CS_CONVECTIVE_INLET
Definition: cs_parameters.h:103
@ CS_FREE_INLET
Definition: cs_parameters.h:100
@ CS_SYMMETRY
Definition: cs_parameters.h:85
@ CS_RAD_TRANSFER_P1
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:56
@ CS_RAD_TRANSFER_DOM
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:55
cs_lnum_t n_b_faces
Definition: cs_mesh.h:99
cs_rad_transfer_model_t type
Definition: cs_rad_transfer.h:134

![]()
![]()
![]() and
and ![]() are given in Kelvin.
are given in Kelvin.![]()
![]() has the value of the flux.
has the value of the flux. ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()