#include <cs_lagr.h>
Data Fields | |
| int | physical_model |
| int | n_temperature_layers |
| int | cs_used |
| int | modcpl |
| int | idistu |
| int | idiffl |
| int | deposition |
| int | dlvo |
| int | roughness |
| int | resuspension |
| int | clogging |
| int | shape |
| int | consolidation |
| int | precipitation |
| int | fouling |
| int | agglomeration |
| int | fragmentation |
| int | n_stat_classes |
| int | n_user_variables |
| bool | viscous_terms |
Main physical model parameters for the Lagrangian module
| int agglomeration |
| int clogging |
| int consolidation |
| int cs_used |
Activates (1) or not (0) the assumption that we are using code_saturne or not. When set to 0 the lagrangian is used within neptune_cfd. When equal to 1, the Lagrangian is used within code_saturne.
| int deposition |
| int dlvo |
| int fouling |
| int fragmentation |
| int idiffl |
| int idistu |
Activation of the turbulent dispersion (on: 1; off). Default is on; This is compatible with RANS and LES turbulent models ( 
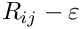

| int modcpl |
Activates (1) or not (0) the assumption that we have regular particles. When set to, 0 then the particles are assumed to be fluid particles (and only the turbulence dispersion model is taken into account by default, but not crossing trajectory effects). Since this model uses volume statistics, is use forces their activation even if not otherwise requested (see idstnt).
| int n_stat_classes |
| int n_temperature_layers |
| int n_user_variables |
| int physical_model |
activates (>0) or deactivates (=0) the physical models associated to the particles:
| int precipitation |
| int resuspension |
| int roughness |
| int shape |
| bool viscous_terms |
Take viscous terms into account