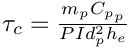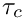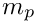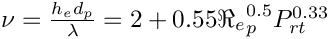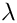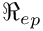Calculation of the particle relaxation time
Modification of the calculation of the particle relaxation time with respect to the chosen formulation for the drag coefficient
This function is called in a loop on the particles, so be careful to avoid too costly operations.
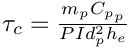
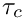 : Thermal relaxation time (value to be computed)
: Thermal relaxation time (value to be computed)
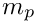 : Particle mass
: Particle mass
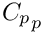 : Particle specific heat
: Particle specific heat
d_p : Particle diameter
h_e : Coefficient of thermal exchange
The coefficient of thermal exchange is calculated from a Nusselt number, itself evaluated by a correlation (Ranz-Marshall by default)
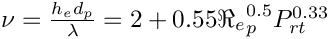
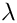 : Thermal conductivity of the carrier field
: Thermal conductivity of the carrier field
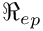 : Particle Reynolds number
: Particle Reynolds number
P_{rt} : Prandtl number
In the next example we compute the relaxation time with two different formulations of the drag coefficient:
void
{
if (re_p <= 1000)
fdr = 18.0 * nu_f * (1.0 + cd1 * pow(re_p, cd2)) / (p_diam * p_diam);
else
fdr = (0.44 * 3.0 / 4.0) * uvwr / p_diam;
taup[p_id] = rho_p / rho_f / fdr;
if (re_p <= rec1)
fdr = 18.0 * nu_f / dd2;
else if (re_p <= rec2)
fdr = 3.0/4.0 * nu_f / dd2 * (22.73 + 0.0903 / re_p + 3.69 * re_p);
else if (re_p <= rec3)
fdr = 3.0/4.0 * nu_f / dd2 * (29.1667 - 3.8889 / re_p + 1.222 * re_p);
else if (re_p <=rec4)
fdr = 18.0 * nu_f / dd2 *(1.0 + 0.15 * pow(re_p, 0.687));
else
fdr = (0.44 * 3.0 / 4.0) * uvwr / p_diam;
taup[p_id] = rho_p / rho_f / fdr;
}
Computation of the thermal relaxation time of the particles
Modification of the computation of the thermal relaxation time of the particles with respect to the chosen formulation of the Nusselt number.
This function is called in a loop on the particles, so be careful to avoid too costly operations.
void
{
cs_real_t fnus = 2.0 + 0.55 * sqrt(re_p) * pow(prt, 1./3.);
tauc[p_id]= diam * diam * rho_p * cp_p / ( fnus * 6.0 * rho_f * cp_f * k_f);
}