|
| integer | ndim |
| | spatial dimension (3) More...
|
| |
| integer, save | ncelet = 0 |
| | number of extended (real + ghost of the 'halo') cells. See Note 1: ghost cells - (halos) More...
|
| |
| integer, save | ncel = 0 |
| | number of real cells in the mesh More...
|
| |
| integer, save | nfac = 0 |
| | number of internal faces (see Note 2: internal faces) More...
|
| |
| integer, save | nfabor = 0 |
| | number of boundary faces (see Note 2: internal faces) More...
|
| |
| integer, dimension(:,:), pointer | ifacel_0 |
| |
| integer, dimension(:), pointer | ifabor_0 |
| |
| double precision, dimension(:,:), pointer | xyzcen |
| | coordinate of the cell centers More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:,:), pointer | surfac |
| | surface vector of the internal faces. Its norm is the surface of the face and it is oriented from ifacel(1,.) to ifacel(2,.) More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:,:), pointer | surfbo |
| | surface vector of the boundary faces. Its norm is the surface of the face and it is oriented outwards More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:,:), pointer | suffac |
| | fluid surface vector of the internal faces. Its norm is the surface of the face and it is oriented from ifacel(1,.) to ifacel(2,.) More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:,:), pointer | suffbo |
| | fluid surface vector of the boundary faces. Its norm is the surface of the face and it is oriented outwards More...
|
| |
| integer, dimension(:), pointer | isolid_0 |
| |
| double precision, dimension(:,:), pointer | cdgfac |
| | coordinates of the centers of the internal faces More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:,:), pointer | cdgfbo |
| | coordinates of the centers of the boundary faces More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:), pointer | volume |
| | volume of each cell More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:), pointer | cell_f_vol |
| | fluid volume of each cell More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:), pointer | surfan |
| | norm of the surface vector of the internal faces More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:), pointer | surfbn |
| | norm of the surface of the boundary faces More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:), pointer | suffan |
| | norm of the fluid surface vector of the internal faces More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:), pointer | suffbn |
| | norm of the fluid surface of the boundary faces More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:), pointer | dist |
| | for every internal face, dot product of the vectors 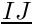 and and 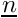 . I and J are respectively the centers of the first and the second neighboring cell. The vector . I and J are respectively the centers of the first and the second neighboring cell. The vector 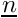 is the unit vector normal to the face and oriented from the first to the second cell More... is the unit vector normal to the face and oriented from the first to the second cell More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:), pointer | distb |
| | For every boundary face, dot product between the vectors 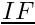 and and 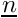 . I is the center of the neighboring cell. F is the face center. The vector . I is the center of the neighboring cell. F is the face center. The vector 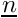 is the unit vector normal to the face and oriented to the exterior of the domain More... is the unit vector normal to the face and oriented to the exterior of the domain More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:), pointer | pond |
| | weighting (Aij=pond Ai+(1-pond)Aj) for every internal face, 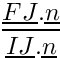 . With regard to the mesh quality, its ideal value is 0.5 More... . With regard to the mesh quality, its ideal value is 0.5 More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:,:), pointer | dijpf |
| | vector I'J' for interior faces for every internal face, the three components of the vector 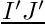 , where I' and J' are respectively the orthogonal projections of the neighboring cell centers I and J on a straight line orthogonal to the face and passing through its center More... , where I' and J' are respectively the orthogonal projections of the neighboring cell centers I and J on a straight line orthogonal to the face and passing through its center More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:,:), pointer | diipb |
| | vector II' for interior faces for every boundary face, the three components of the vector 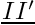 . I' is the orthogonal projection of I, center of the neighboring cell, on the straight line perpendicular to the face and passing through its center More... . I' is the orthogonal projection of I, center of the neighboring cell, on the straight line perpendicular to the face and passing through its center More...
|
| |
| double precision, dimension(:,:), pointer | dofij |
| | vector OF for interior faces for every internal face, the three components of the vector 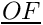 . O is the intersection point between the face and the straight line joining the centers of the two neighboring cells. F is the face center More... . O is the intersection point between the face and the straight line joining the centers of the two neighboring cells. F is the face center More...
|
| |