|
programmer's documentation
|
|
programmer's documentation
|
The module can be activated in the usppmo routine in cs_user_parameters.f90. The corresponding keyword is iirayo in the cs_glob_rad_transfer_params structure.
This member can take the values:
When the module is activated, its specific input parameters should be set in the cs_user_radiative_transfer_parameters function of the cs_user_radiative_transfer.c file.
Radiative transfer parameters may be defined using the cs_user_radiative_transfer_parameters function.
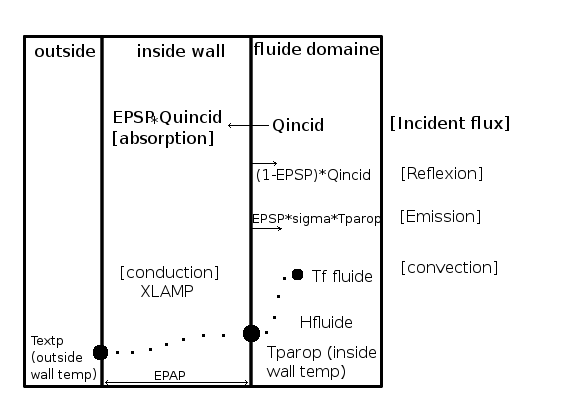
The radiative boundary condition is based on the calculation of a new wall temperature. This temperature is computed with a thermal flux balance:
![\[{ Q_{conduction} = Q_{convection} + (Q_{rayt_{absorption}} - Q_{rayt_{emission}}}) \]](form_709.png)
Therefore :
![\[ \dfrac{xlamp}{epap} (T_{fluid} - T_{wall}) = h_{fluid} (T_{fluid} - T_{wall}) + epsp (Q_{incid} - \sigma * T_{wall}) \]](form_710.png)
Code_Saturne the flux is positive when it is oriented from inside to outside.| Body | Emissivity |
|---|---|
| polished steel | 0.06 |
| oxidized steel | 0.80 |
| steel rough | 0.94 |
| polished aluminium | 0.04 |
| oxidiezd aluminium (inside) | 0.09 |
| oxidized aluminium (wet air) | 0.90 |
| brick | 0.93 |
| concrete | 0.93 |
| paper | 0.8 to 0.9 |
| water | 0.96 |
Boundary faces may be identified using the getfbr function, or preferrably, through boundary zones, defined using the GUI or the cs_user_zones function..
The following declaration and initialization block needs to be added for the following examples:
Remaining initialisation
ivar: number of the thermal variable
Min and Max values for the wall temperatures (clipping otherwise)
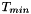 and
and 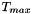 are given in Kelvin.
are given in Kelvin.
For each boundary face face_id, a specific output (logging and postprocessing) zone id may be assigned. This allows realizing balance sheets by treating them separately for each zone. By default, the output zone id is set to the general (input) zone id associated to a face.
To access output zone ids (both for reading and modifying), use the cs_rad_transfer_get_output_b_face_zone_ids function. The zone id values are arbitrarily chosen by the user, but must be positive integers; very high numbers may also lead to higher memory consumption.
 1.8.13
1.8.13