Variables | |
| char * | mpi_rank_id_cells |
| char * | mpi_rank_id_interior_faces |
| char * | mpi_rank_id_boundary_faces |
| char * | mpi_rank_id_vertices |
| char * | r_gen_cells |
| char * | r_gen_interior_faces |
| char * | r_gen_boundary_faces |
| char * | r_gen_vertices |
| char * | boundary_zone_class_id |
| char * | boundary_stress |
| char * | boundary_stress_normal |
| char * | boundary_stress_tangential |
| char * | boundary_thermal_flux |
| char * | boundary_nusselt |
| char * | relative_pressure |
| char * | relative_velocity |
| char * | absolute_pressure |
| char * | absolute_velocity |
| char * | elec_pot_gradient_im |
| char * | elec_current_gradient_im |
| char * | elec_pot_module |
| char * | elec_pot_arg |
| char * | q_criterion |
Note that a function object of a given name may always be accessed using cs_function_by_name.
| char* absolute_pressure |
Absolute pressure (at cells) with Corilolis forces.
Automatically activated when Coriolis forces are present.
| char* absolute_velocity |
Absolute velocity (at cells) with Coriolis forces.
Automatically activated when Coriolis forces are present.
| char* boundary_nusselt |
Boundary layer Nusselt number. This is based only on the near-boundary temperature value and heat flux, so does not require a bulk temperature value but is not a "true" Nusselt number computation, as the fluid value used may be sensitive to mesh refinement.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* boundary_stress |
Stress exerted by fluid forces over boundary. Activating this function also leads to the creation of the "boundary_stress" field, used to store and update the boundary stress vector.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* boundary_stress_normal |
Normal component of the stress exerted by fluid forces over boundary. Activating this function also leads to the creation of the "boundary_stress" field, used to store and update the boundary stress vector.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* boundary_stress_tangential |
Tangential component of the stress exerted by fluid forces over boundary. Activating this function also leads to the creation of the "boundary_stress" field, used to store and update the boundary stresses.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* boundary_thermal_flux |
Thermal flux density over the boundary. Incoming thermal flux leads to a positive sign; outgoing thermal flux to a negative sign.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* boundary_zone_class_id |
Optional boundary face class or zone ids. If no face classes have been defined by cs_boundary_zone_face_class_id, the boundary face zone id is used instead.
Activated by default.
| char* elec_current_gradient_im |
For Joule Heating by direct conduction, imaginary component of the current density
Automatically activated when Joule Heating by direct conduction is active cs_glob_physical_model_flag[CS_JOULE_EFFECT] == 2 or 4.
| char* elec_pot_arg |
For Joule Heating by direct conduction, argument of the complexe potential.
Automatically activated when Joule Heating by direct conduction is active cs_glob_physical_model_flag[CS_JOULE_EFFECT] == 4.
| char* elec_pot_gradient_im |
For Joule Heating by direct conduction, gradient of the imaginary component of the potential.
Automatically activated when Joule Heating by direct conduction is active cs_glob_physical_model_flag[CS_JOULE_EFFECT] == 2 or 4.
| char* elec_pot_module |
For Joule Heating by direct conduction, module of the complexe potential.
Automatically activated when Joule Heating by direct conduction is active cs_glob_physical_model_flag[CS_JOULE_EFFECT] == 4.
| char* mpi_rank_id_boundary_faces |
MPI rank id to which boundary faces are assigned. This rank is always the same as the adjacent cell.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* mpi_rank_id_cells |
MPI rank id to which a cell is assigned.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* mpi_rank_id_interior_faces |
MPI rank id to which interior faces are assigned. Interior faces at parallel boundaries are seen from 2 domains, but may be assigned specifically to one domain when range sets (cs_range_set_t) are used. If no range set has already been assigned to interior faces, a default one (ignoring periodicity) is used. Otherwise (such as when using CDO face-based schemes), the one actually used for computation is used.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* mpi_rank_id_vertices |
MPI rank id to which vertices are assigned. Vertices at parallel boundaries are seen from multiple, but may be assigned specifically to one domain when range sets (cs_range_set_t) are used. If no range set has already been assigned to vertices, a default one (ignoring periodicity) is used. Otherwise (such as when using CDO vertex-based schemes), the one actually used for computation is used.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* q_criterion |
Compute the Q criterion from Hunt et. al.
![\[ Q = \tens{\Omega}:\tens{\Omega} -
\deviator{ \left(\tens{S} \right)}:\deviator{ \left(\tens{S} \right)}
\]](form_786.png)
where 
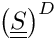
Accessed or activated using:
| char* r_gen_boundary_faces |
Refinement generation of boundary faces. This should always be that of the adjacent cell.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* r_gen_cells |
Refinement generation of mesh cells. This is considered to be the highest refinement level of adjacent interior faces.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* r_gen_interior_faces |
Refinement generation of interior faces. This is determined and stored when refining or coarsening a mesh. A refined face's sub-faces have the same refinement generation as their parent. Faces added in the course of refinement (i.e. faces separating sub-cells) have a refinement level one higher than the parent cell.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* r_gen_vertices |
Refinement generation of vertices. This is determined and stored when refining or coarsening a mesh.
Accessed or activated using:
| char* relative_pressure |
Relative pressure (at cells) for turbomachinery computations.
Automatically activated for turbomachinery computations.
| char* relative_velocity |
Relative velocity (at cells) for turbomachinery computations.
Automatically activated for turbomachinery computations.